
Catalysis is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst

A chemical synthesis begins by selection of compounds that are known as reagents or reactants.
Improved nanotechnology catalysts bring clean energy applications closer.

Zeolites are microporous, aluminosilicate minerals & they have porous structure that can accommodate a variety of cation

The enthalpy of reaction is the heat absorbed at steady T and P.

Catalysis is the process of increasing rate of chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst.

Heterogeneous catalysts, Electrocatalysts, Homogeneous catalysts, Organocatalysis, Photocatalysts, Tandem catalysis
Environmental & Green chemistry focuses on effects of polluting chemicals on nature & environmental impact of chemistry

• Chemical engineering for renewables conversion • Control and optimisation of process systems • Fuel cell technologies
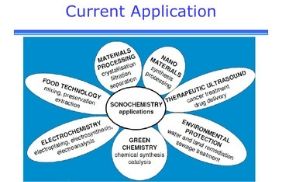
• Chemistry in computing • Chemistry in the space age • Chemistry in fibre and paper technology • Waste water management

Polymerization is the process of combination of small biochemical molecules known as monomers into a bonded chain.

• Process Systems Engineering • Catalysis in oil & gas • Biocatalysis & Biotransformations • Separation & Bioseparation

It focuses on the structure, operation, control, optimization & intensification of chemical, physical biological process

Materials Engineering is the design and discovery of new materials, particularly solids.